γ -spectroscopy group
The Gamma Spectroscopy group performs nuclear structure studies using stable beams provided by the PIAVE-ALPI-TANDEM accelerators of Legnaro National Laboratory, and high-resolution Ge arrays coupled to different ancillary detectors. The group works in close collaboration with the "Galileo Galilei" physics department of the University of Padova and INFN-Padova. Furthermore, the group belongs to the GAMMA collaboration for nuclear physics. This collaboration is part of the INFN - National Scientific Committee 3 (CSN3) initiative, which involves 5 INFN divisions: INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro (LNL),
- INFN - Sezione di Firenze (FI),
- INFN - Sezione di Milano (MI),
- INFN - Sezione di Padova (PD),
- University of Camerino.
The group is also involved with SPES, which is a next generation ISOL-type accelerator that together with the operation of existing machines, is the future of LNL. SPES will provide Radioactive Ion Beam for nuclear physics and astrophysics research, as well as for interdisciplinary applications.
Currently, the AGATA array is being employed to detect γ radiation emitted after reactions such as fusion-evaporation, and low-energy Coulomb excitation. You can find more information on the installation and performance of AGATA@LNL here. At the moment, GALILEO, the native array for detection γ-ray radiation, is not operational as all efforts are focused on AGATA.
The physics program of the group is focused, but not limited, on following topics:
- Shell structure in n-rich nuclei
- Isospin symmetries and n-p pairing
- Pigmy resonance of interest in astrophysics
- Structure of nuclei at the proton-drip line
- Critical points and phase transitions between different nuclear shapes
In addition to the local activities, the group also performs research in collaboration with different laboratories such as GANIL, ISOLDE, JYU, the RIKEN Nishina Center, and GSI which is at the moment evolving into FAIR .
AGATA@LNL
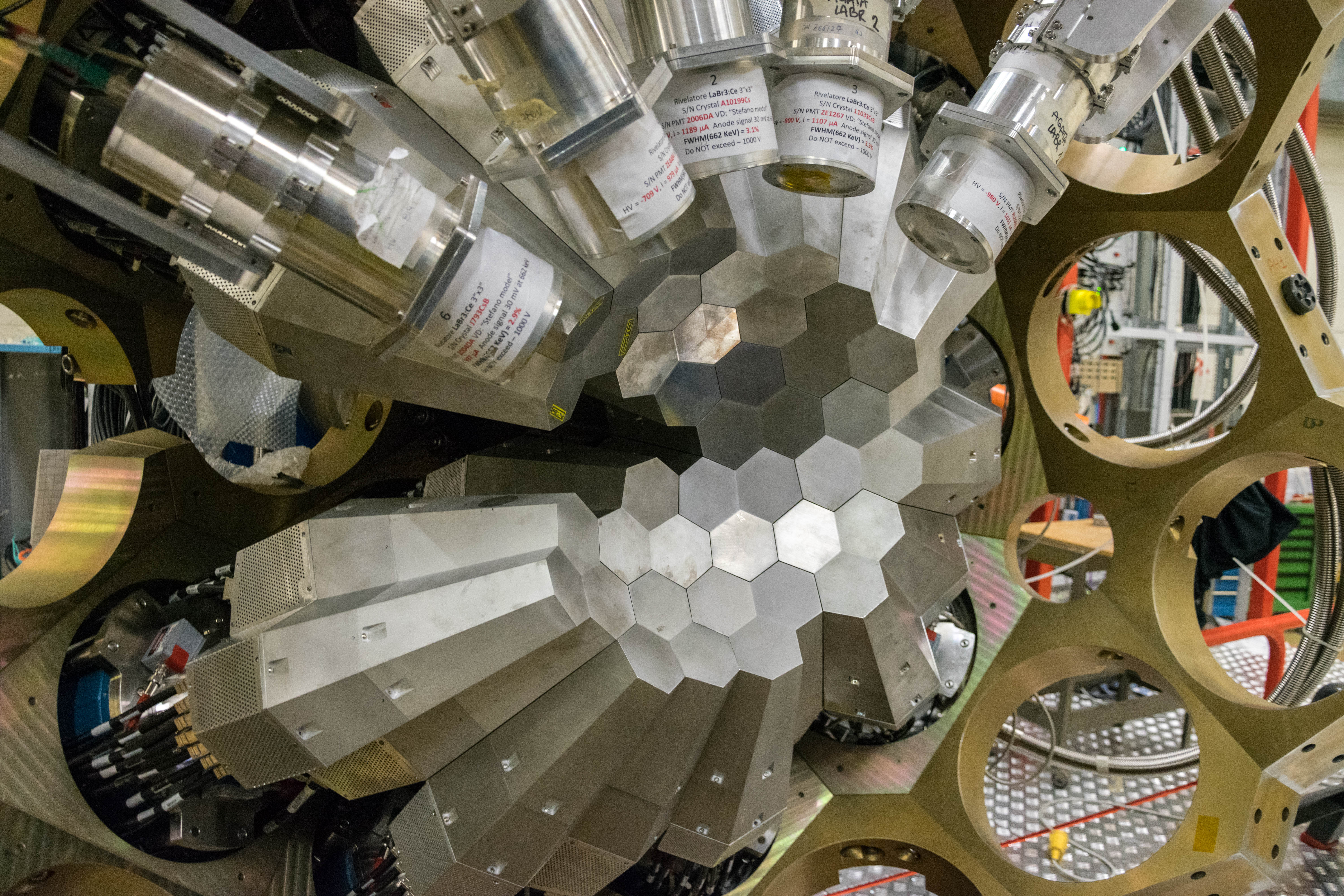
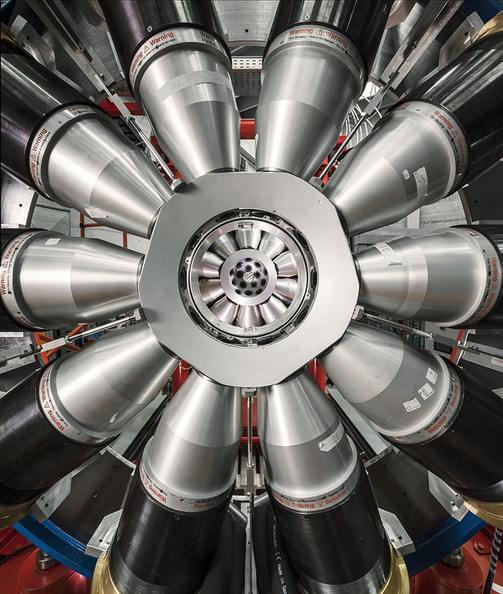
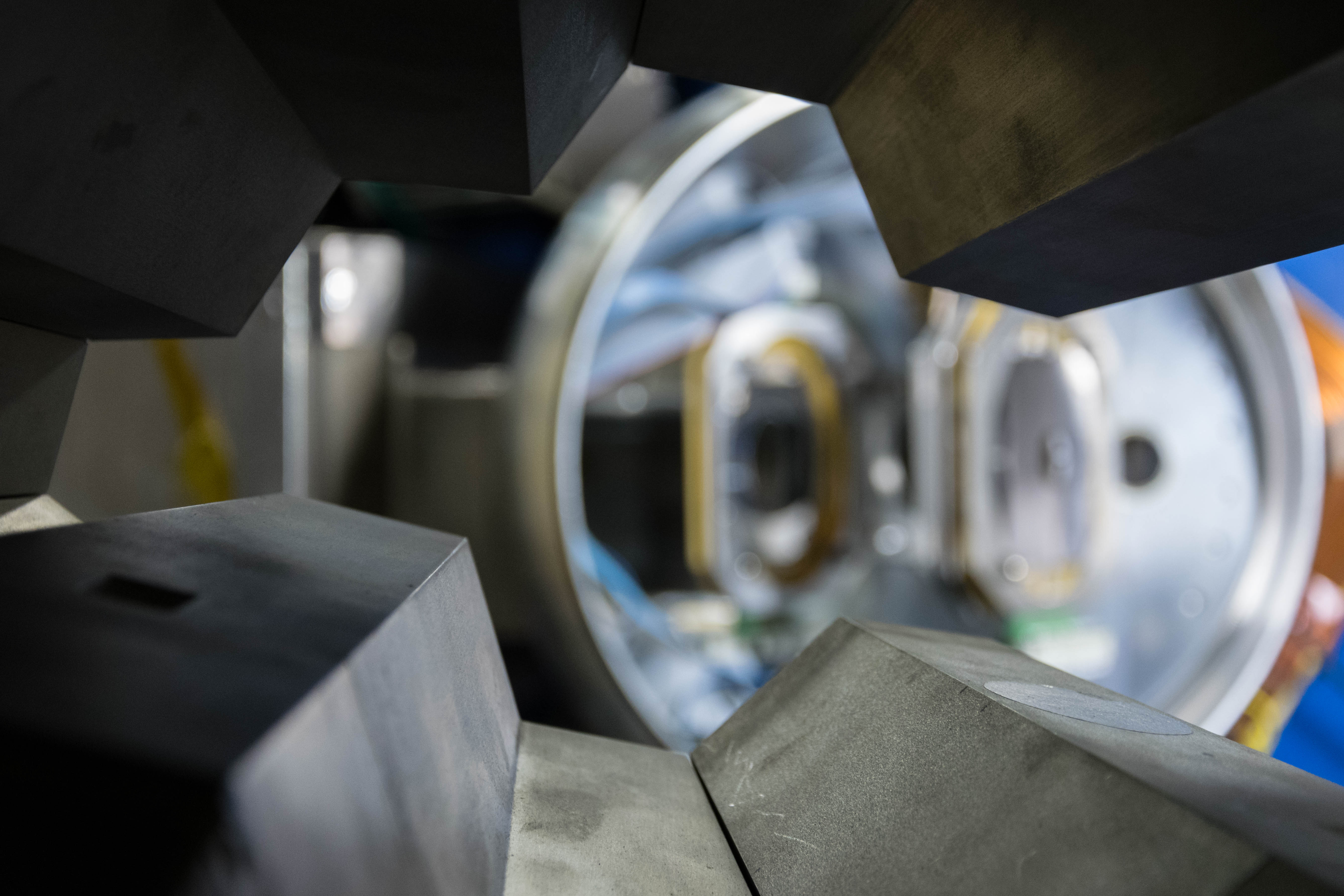
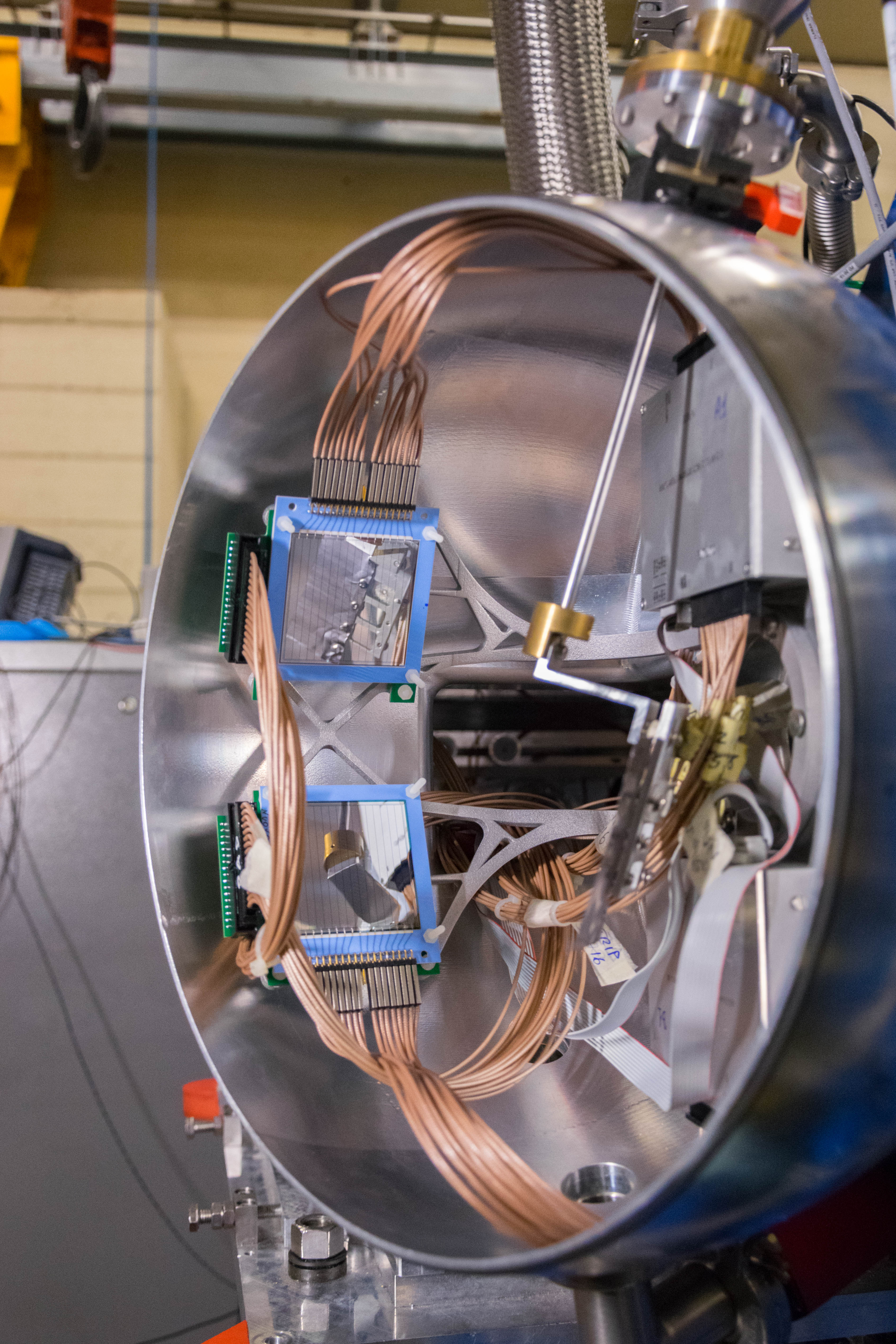
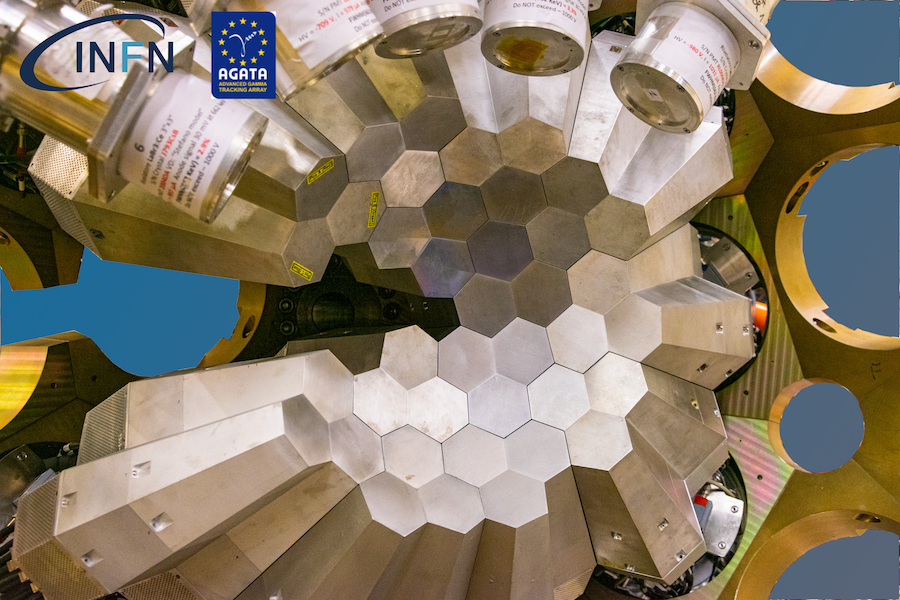
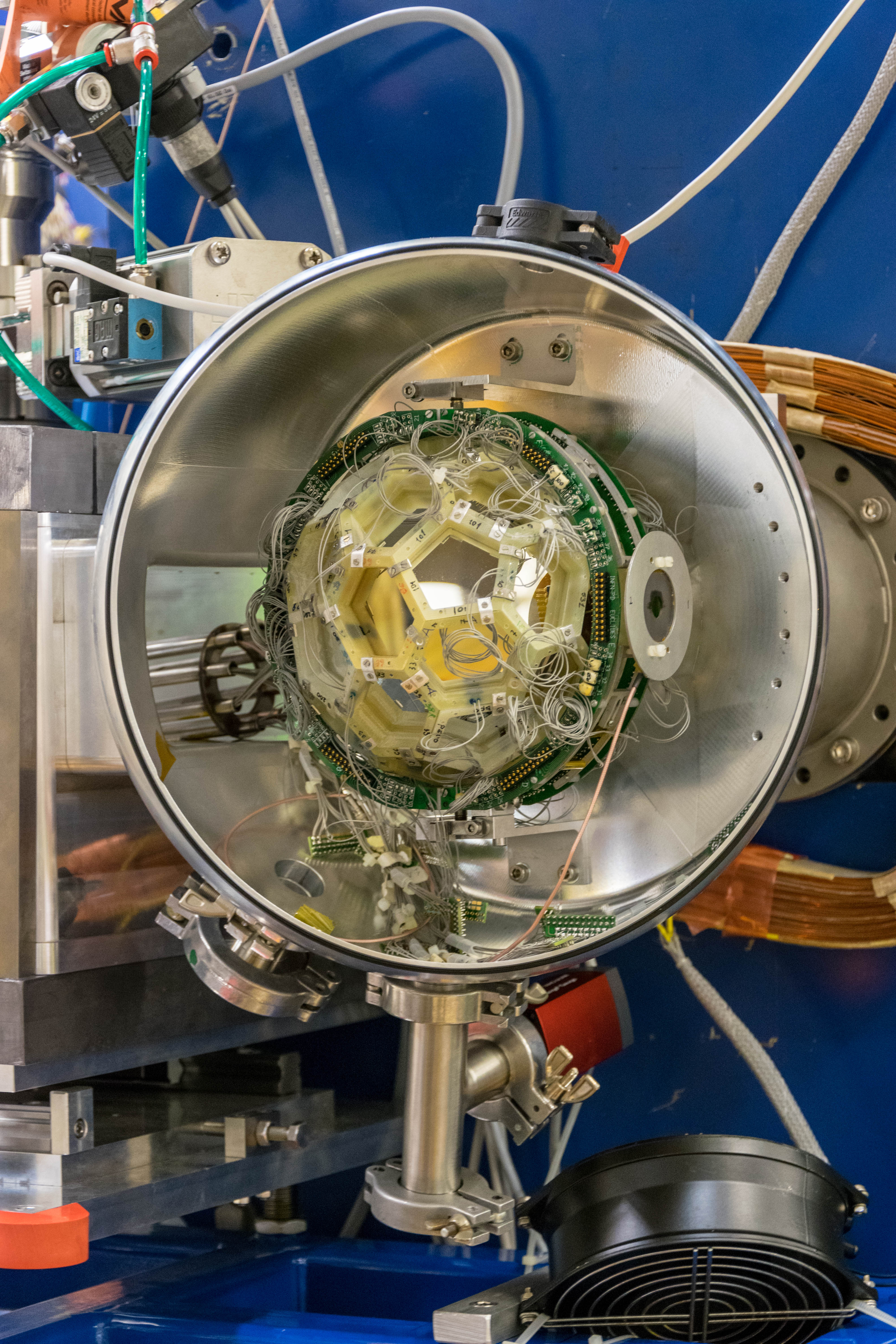
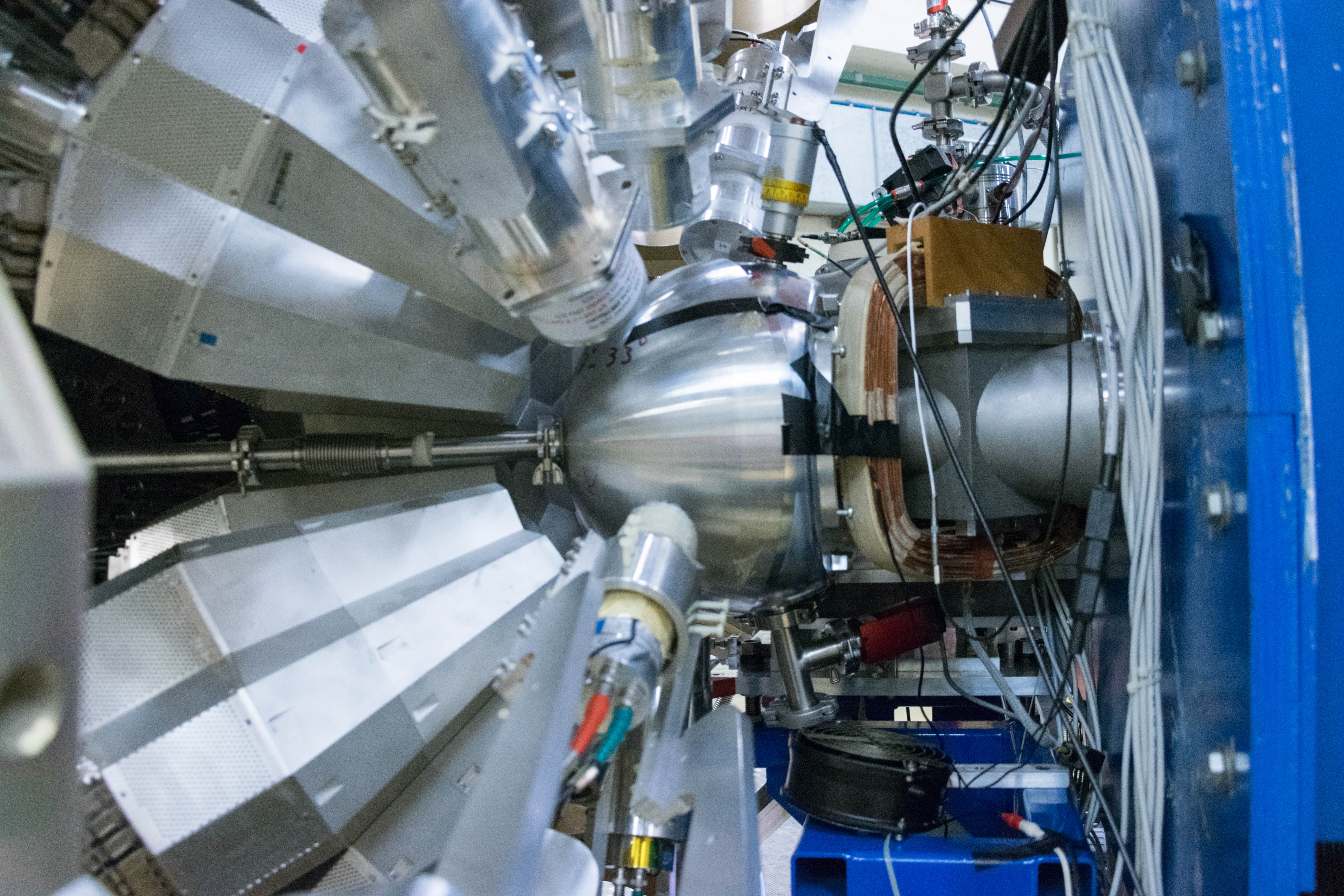
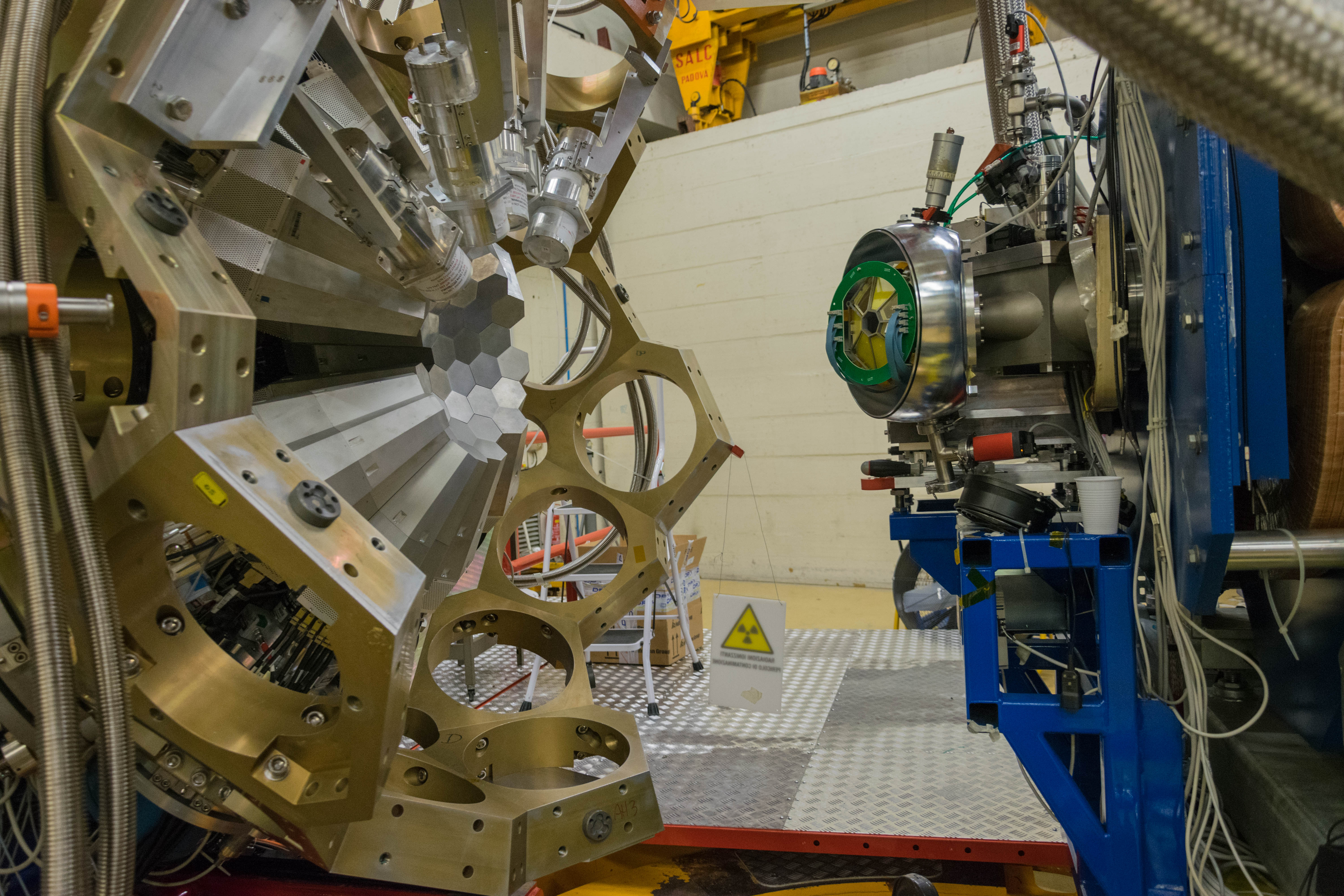
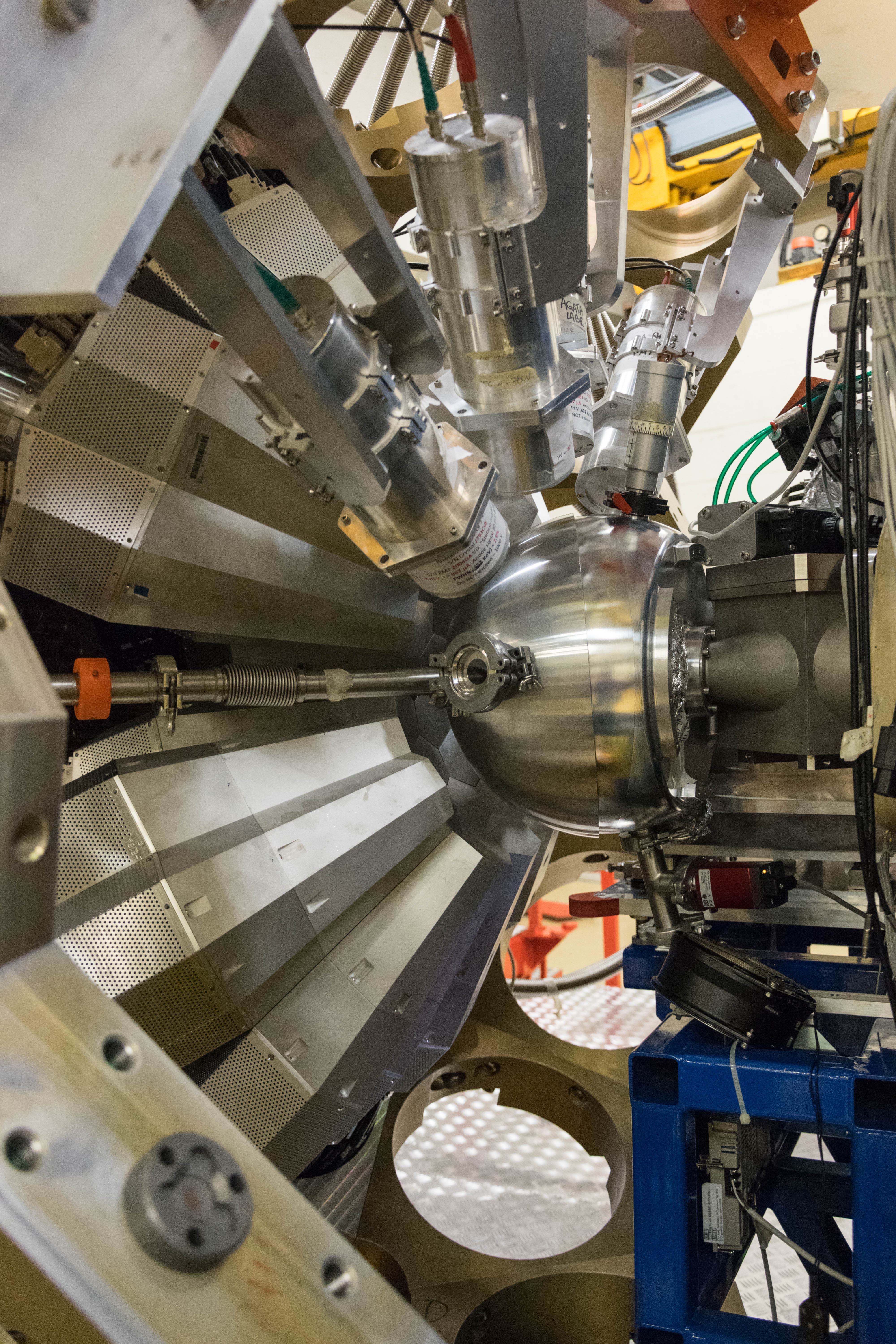
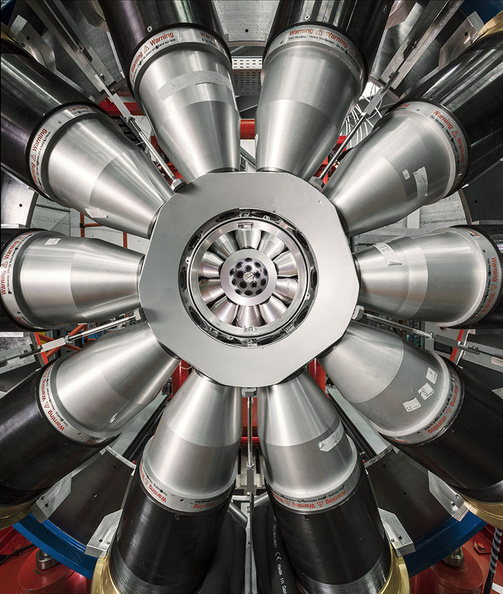
AGATA (Advanced GAmma Tracking Array) is a highly segmented High Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector array. It is a European collaboration project funded by twelve countries in Europe. The project was proposed in 2001 and in 2002 it was signed by the participant countries. AGATA is capable of high counting event rates and can be coupled with ancillary detectors, such as magnetic spectrometers, fast-timing detectors charged particles or neutron detectors. The AGATA detectors are Ge-detectors that are 36-fold segment with six-fold azimuthal and six-fold longitudinal segmentation.
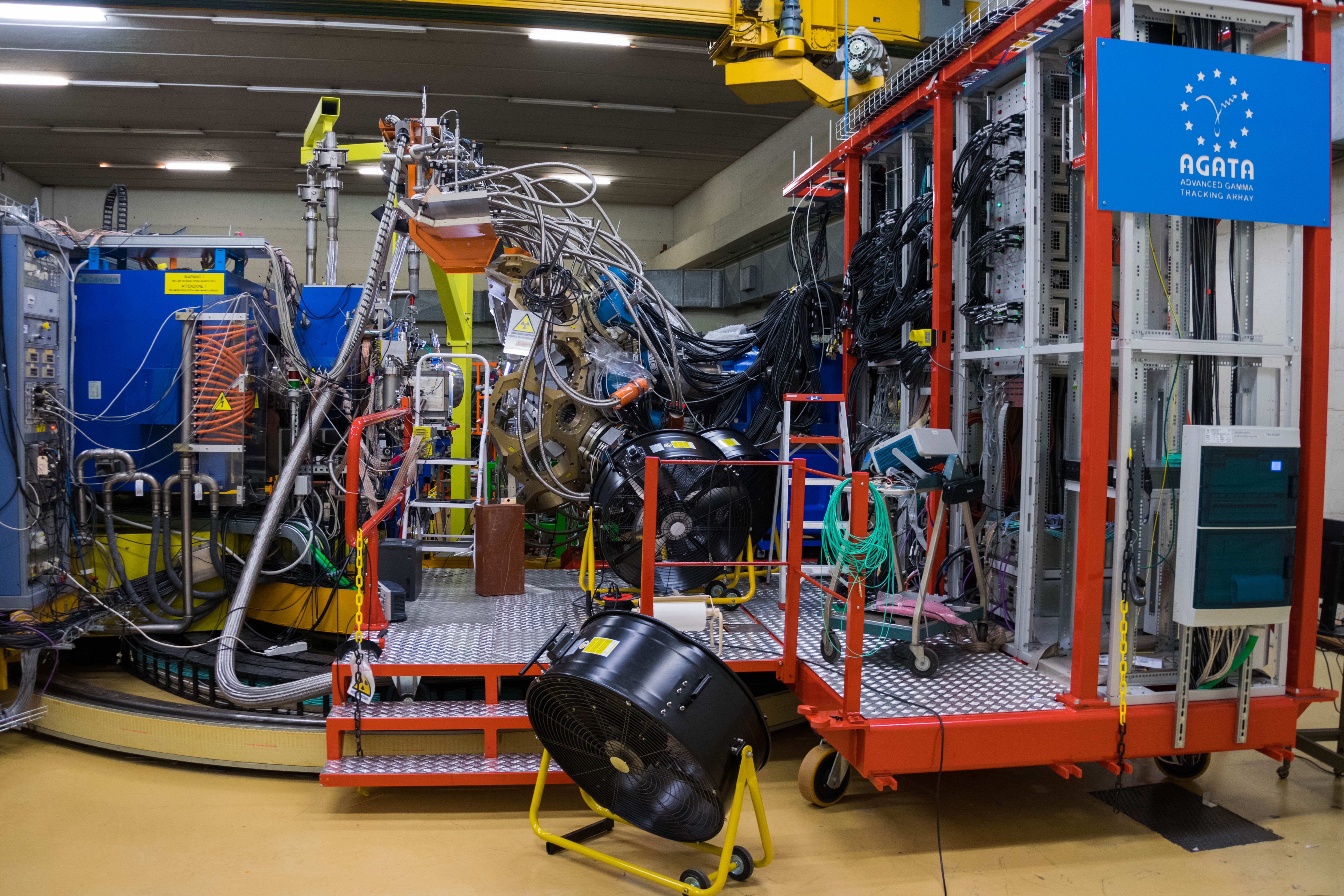
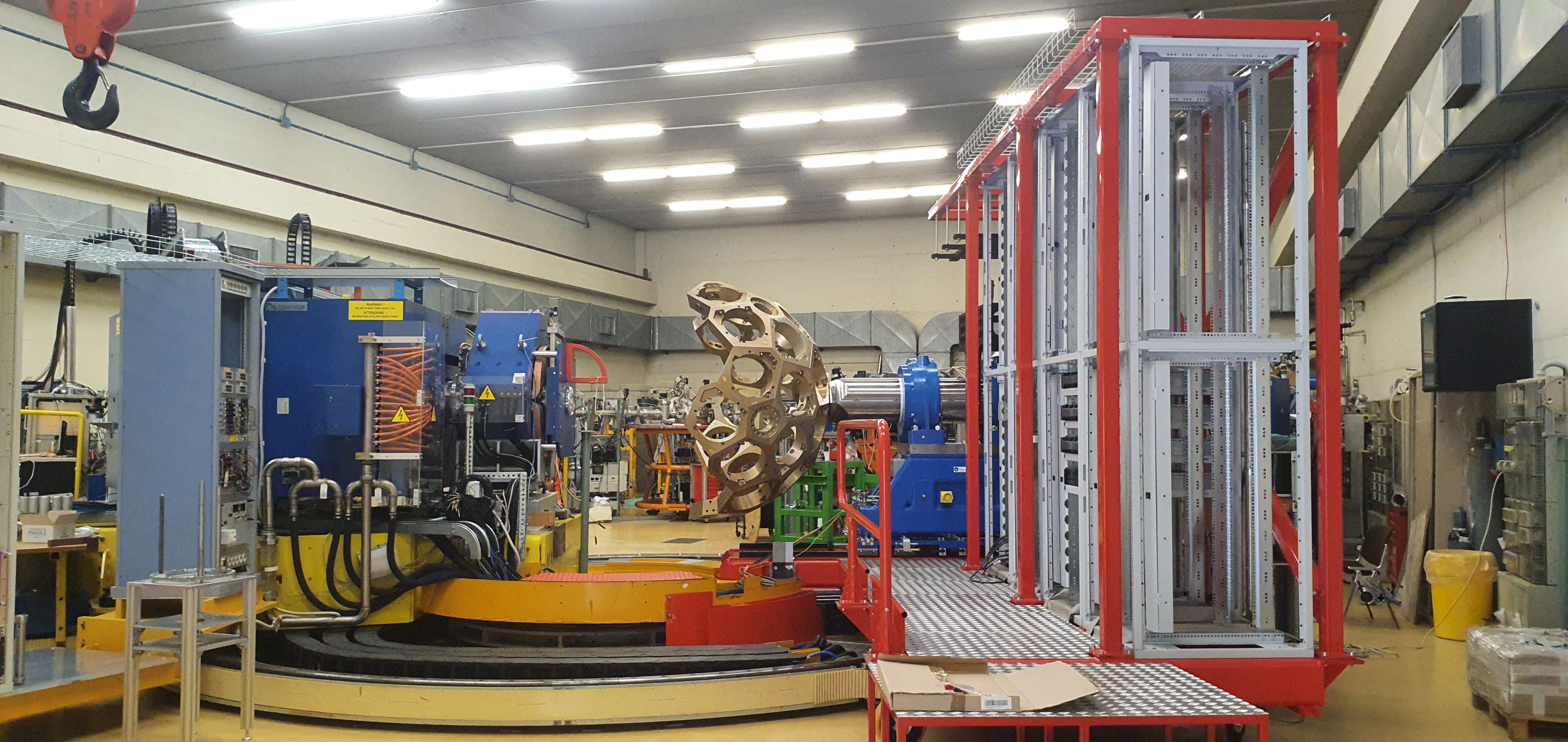
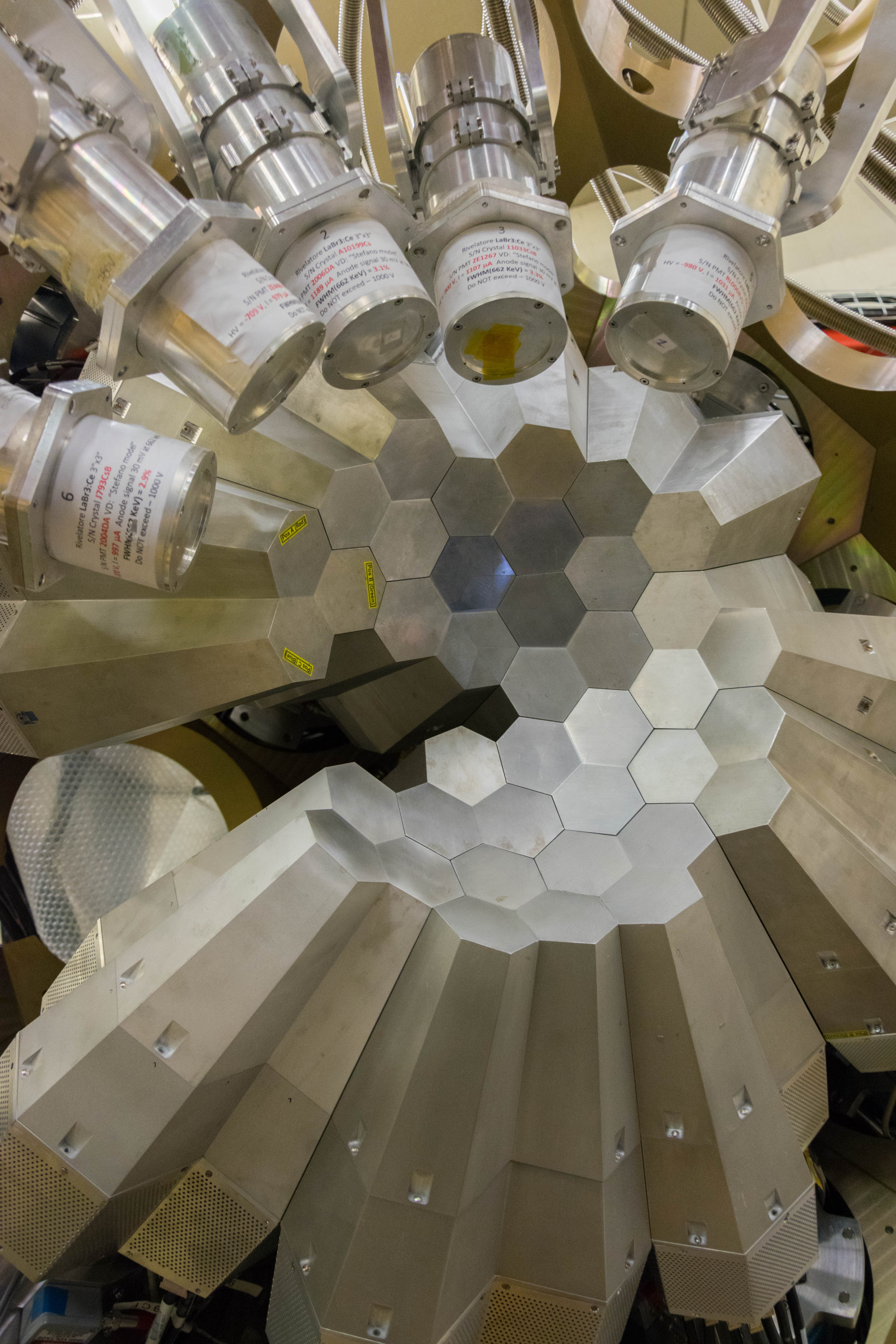
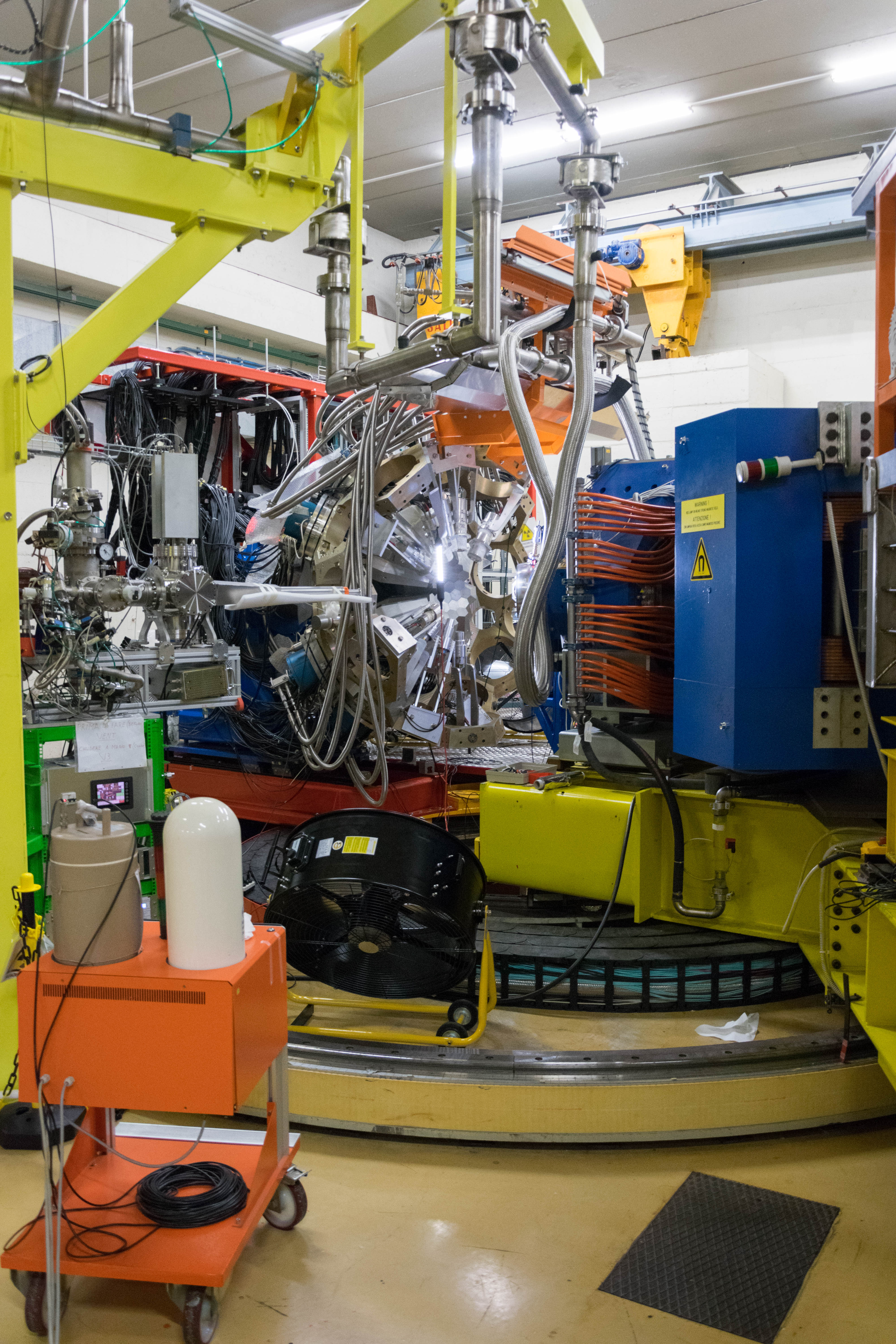
Since 2022, AGATA array is installed in the Legnaro Laboratories, where it is coupled to the magnetic spectrometer PRISMA. AGATA array is complemented by 9 LaBr3 detectors. Throughout the campaigns in 2022 and 2023, a total of 27 experiments were carried out using AGATA. Detailed description of AGATA setup at LNL, data acquisition system and complementary instrumentation is given in NIM A paper.
Performance figures of AGATA obtained during the 2022 campaign were published in Legnaro Annual Reports here and here. Note that the additional shielding was present in front of AGATA during this evaluation, details are given in the reports.
AGATA installation at LNL, 2022
Photos
Additional pictures from the AGATA campaign can be found here, pictures taken by M. Balogh.
GALILEO
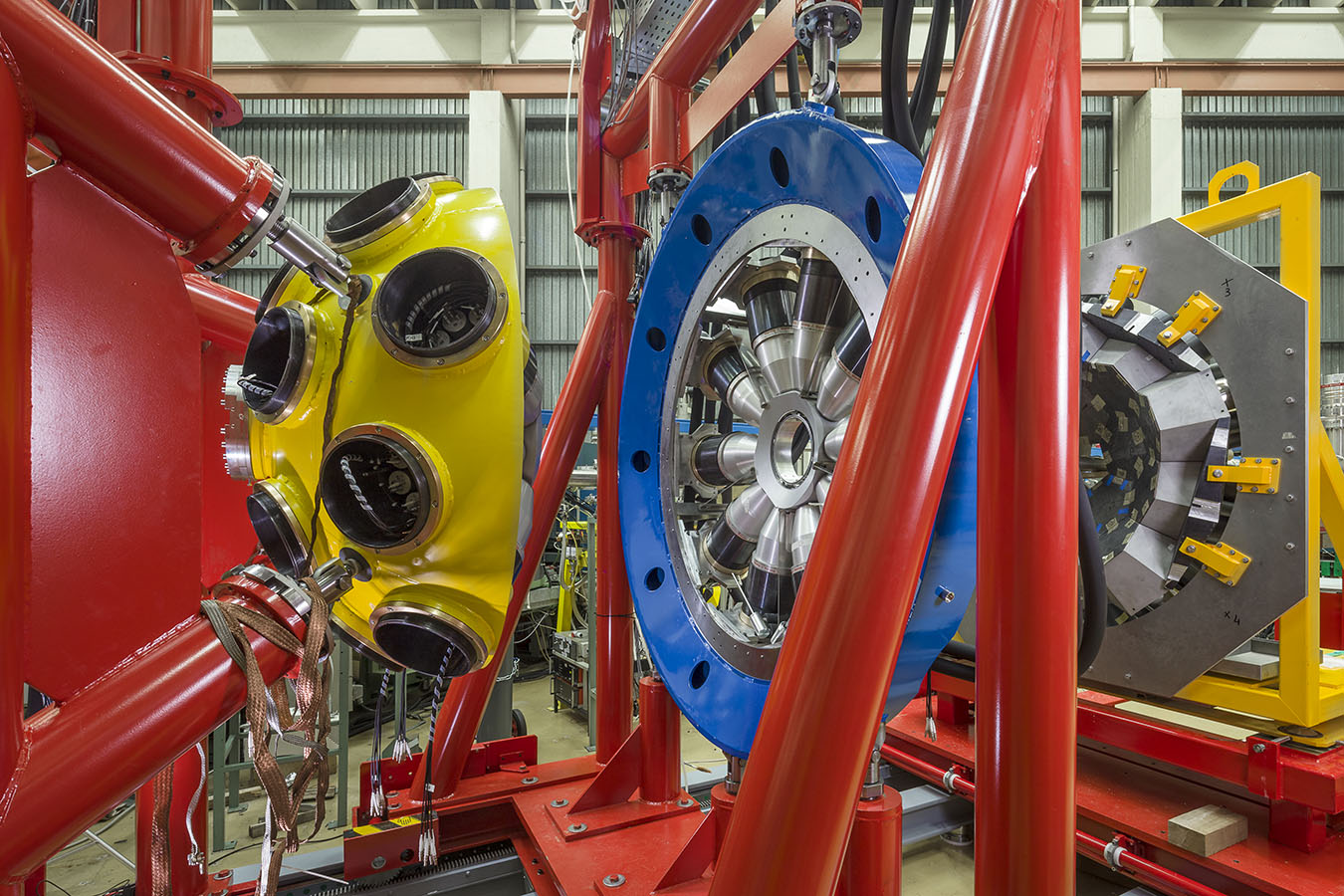
GALILEO (Gamma Array of Legnaro INFN Laboratories for nuclEar spectrOscopy) is the current high-resolution Ge array for advanced in-beam γ-ray spectroscopy studies constructed and installed at LNL.
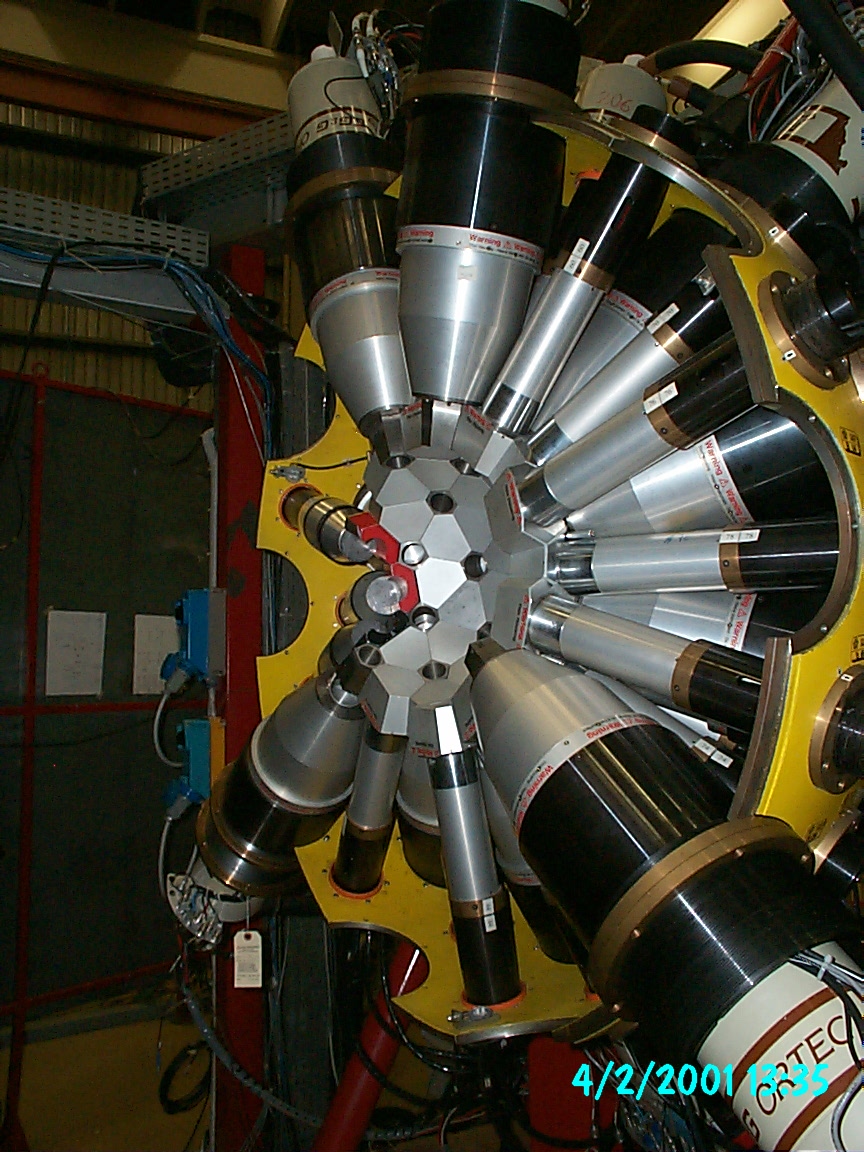
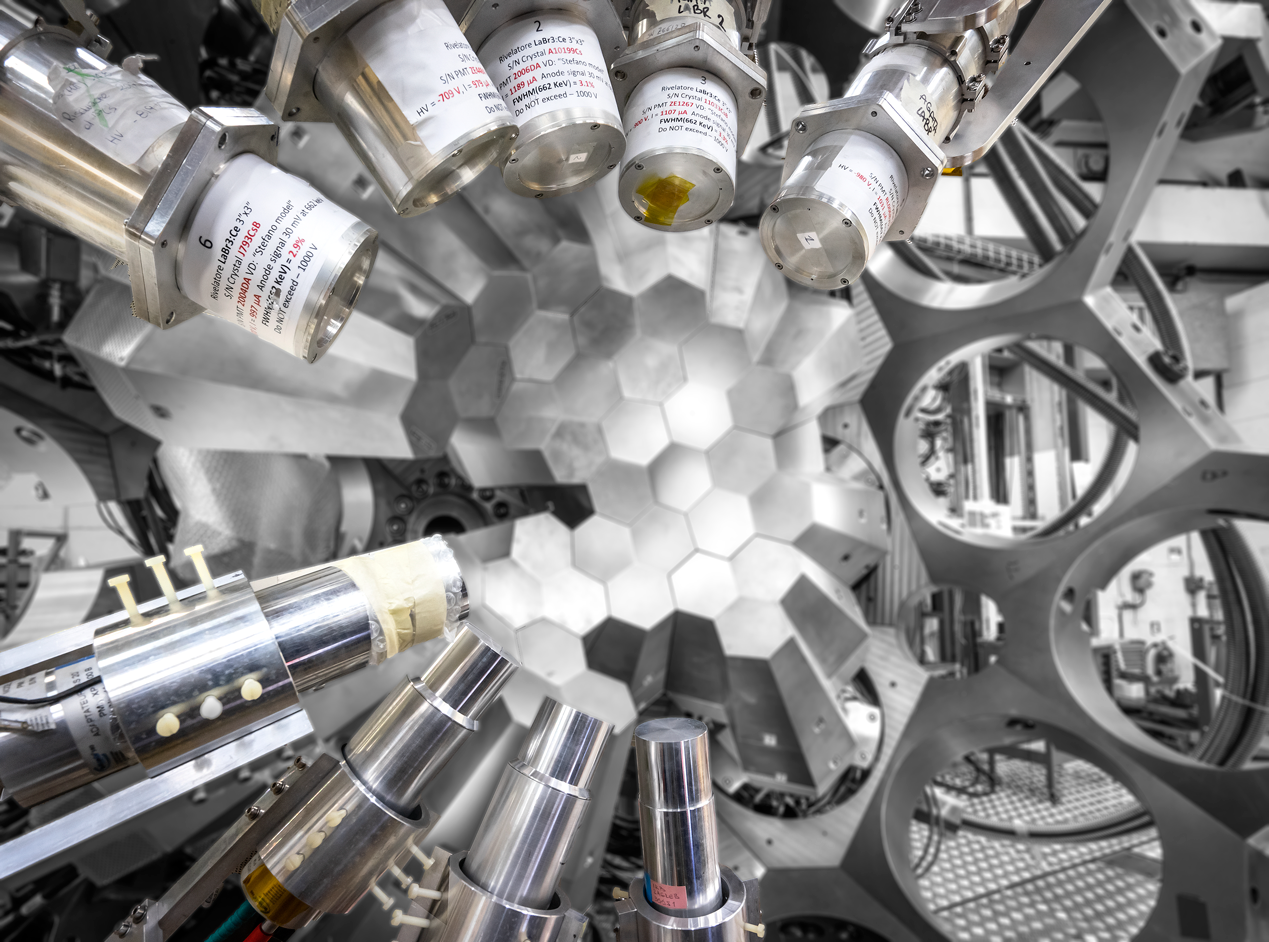
The first phase of GALILEO was operational between 2015 and 2019 and consisted of 25 GASP tapered detectors coupled to Neutron Wall as shown in the picture. In a second stage of this phase, 10 GASP detectors were moved to the forward angles (replacing Neutron Wall) and LaBr3 detectors were mounted at 90° to optimize the setup for measurements using the Plunger.
In its second phase, GALILEO will consist of 25 GASP tapered detectors at 90° and forward angles, and 10 triple clusters built using capsules of EUROBALL, mounted at backward angles. At the moment 20 GASP detectors and one triple cluster are mounted in the structure. Keep updated on the progress of the array following the latest news.
The HPGe detectors are surrounded by anti-Compton shields in order to reach, for the whole array, a peak-to-total ratio of about 55%. A 5cm thick heavy-metal shield improves Compton rejection, avoiding direct γ -ray interactions in the BGO shields. The geometry of the array is designed to maximize the photo-peak efficiency under typical in-beam medium-high γ-ray multiplicity conditions, achieving a value of 6.4%. GALILEO can be coupled to different ancillary devices.
Check out the list of GALILEO physics publications, or take a look at some of the technical publications . You can also see previous thesis regarding GALILEO or its ancillary devices.
A full list of the experiments approved and performed with GALILEO can be found here

Previous Arrays
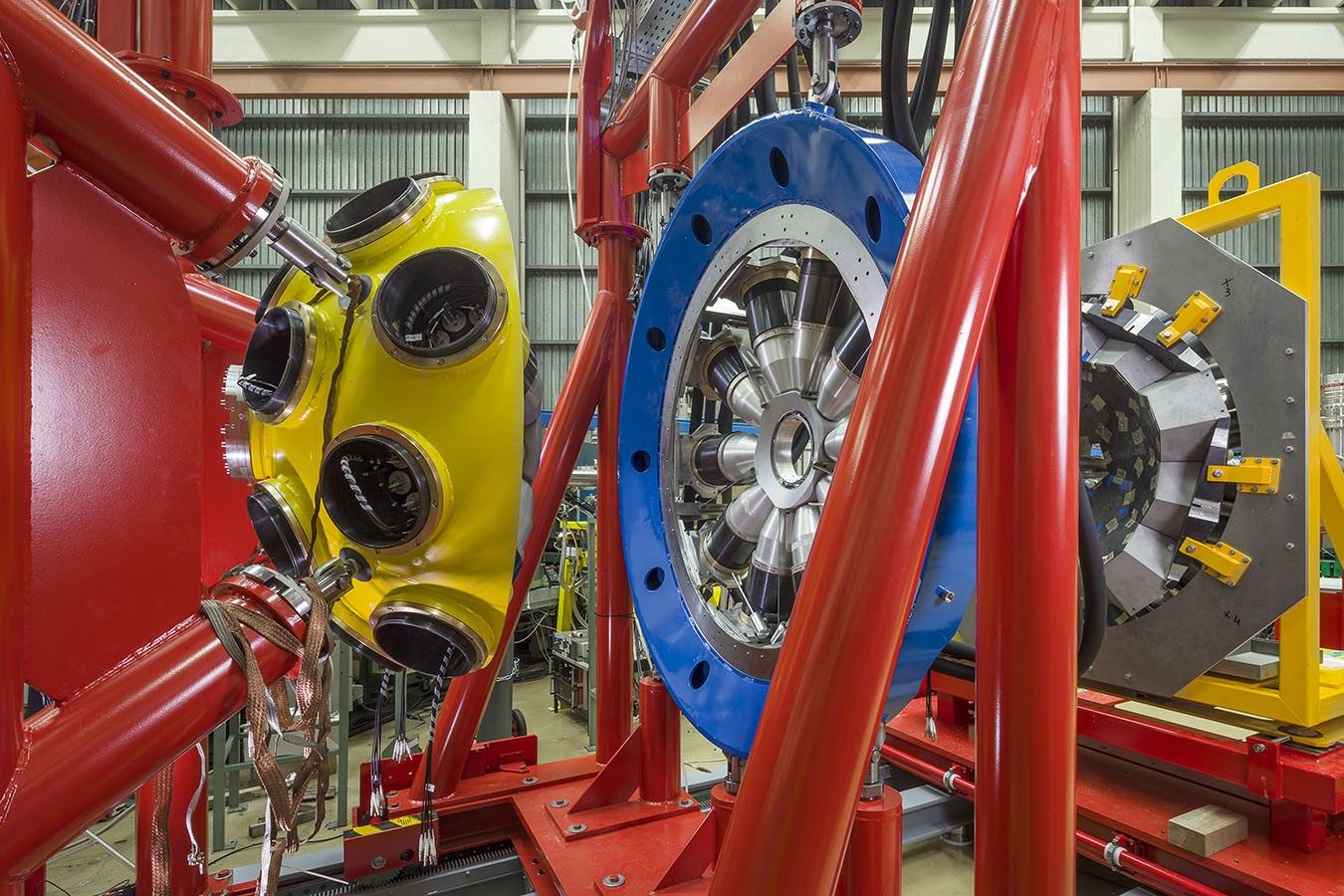
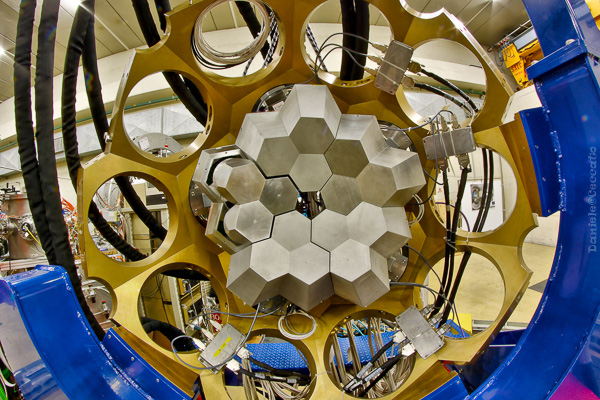
The group has a well-established expertise in nuclear spectroscopy with high-resolution gamma-arrays. Since the first experiments performed in the 90s, the group has hosted GASP, EUROBALL, CLARA, as well as the first stage of the last-generation European gamma-array, the AGATA demonstrator.

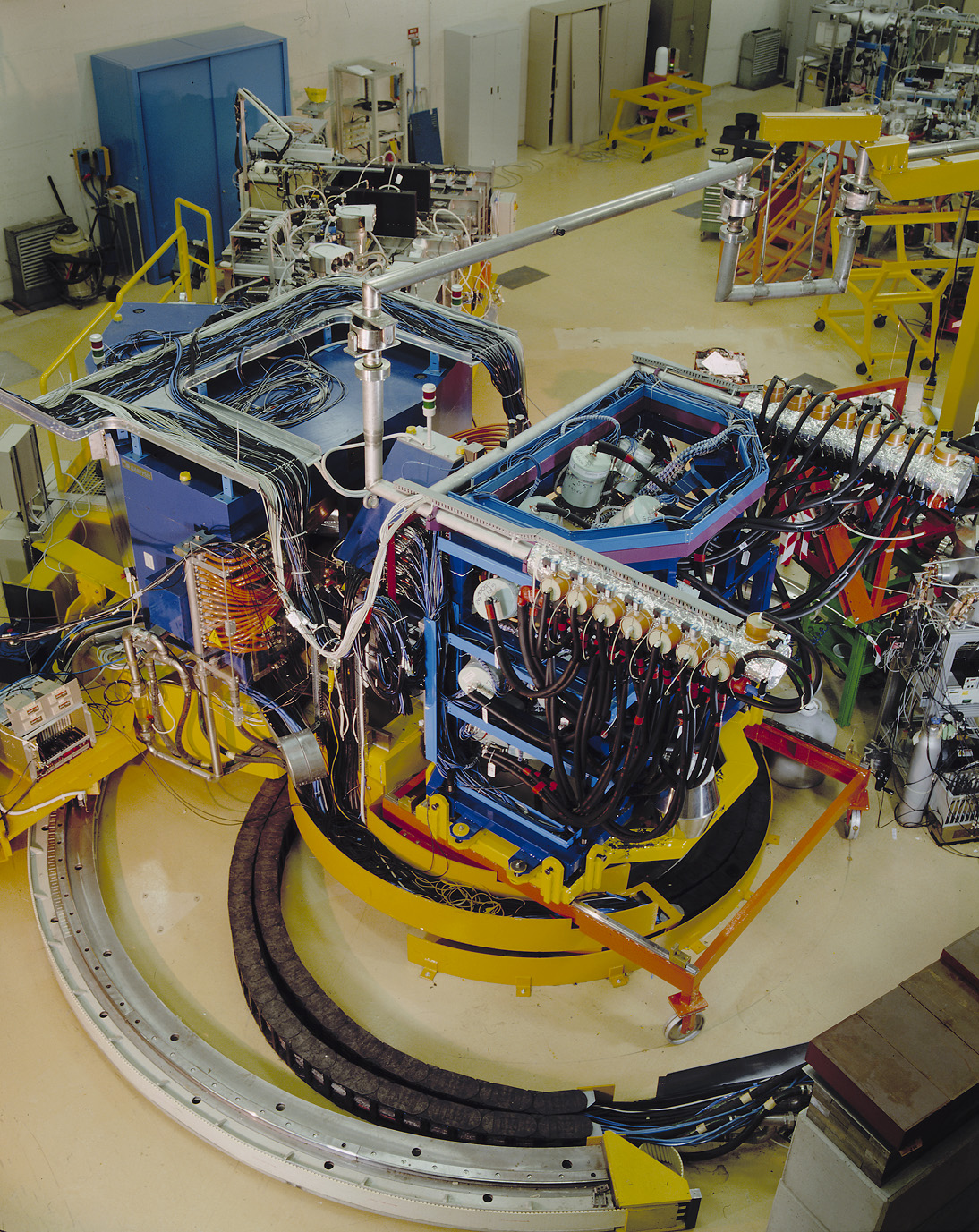

Ancillary devices
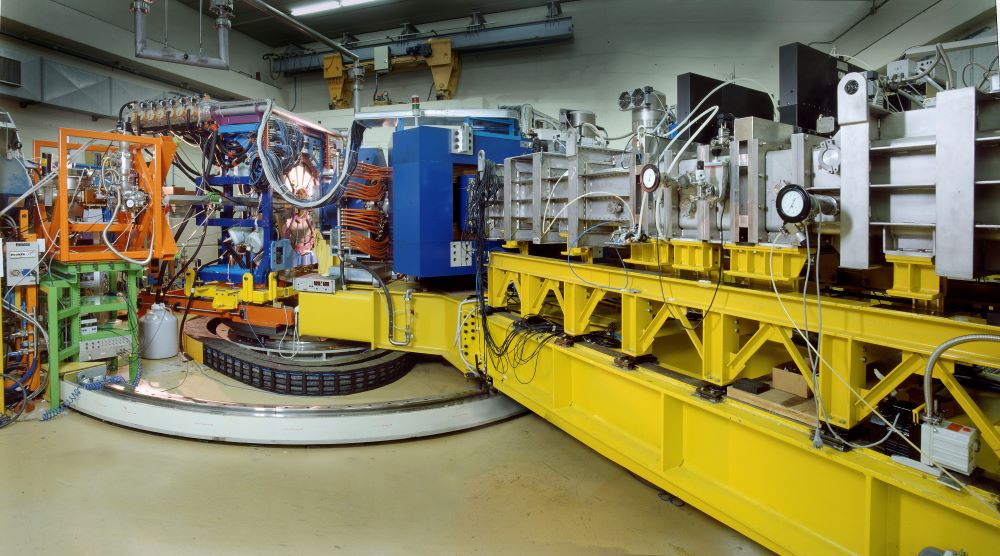

PRISMA
PRISMA is a large-acceptance magnetic spectrometer for heavy ions. Its design is based on a simple quadrupole-dipole configuration, with no hardware elements correcting for the optical aberrations, which are corrected instead via a software reconstruction of the trajectories of the nuclei inside the spectrometer. The trajectories are deduced from the point of entrance in the spectrometer and in the focal plane, where position-sensitive detectors are placed. The start detector of PRISMA is based on an MCP, while the focal plane detector is based on a MWPPAC. These detectors provide also a time-of-flight measurement. An ionisation chamber placed after the MWPPAC measures the charge and total energy of the incoming ions.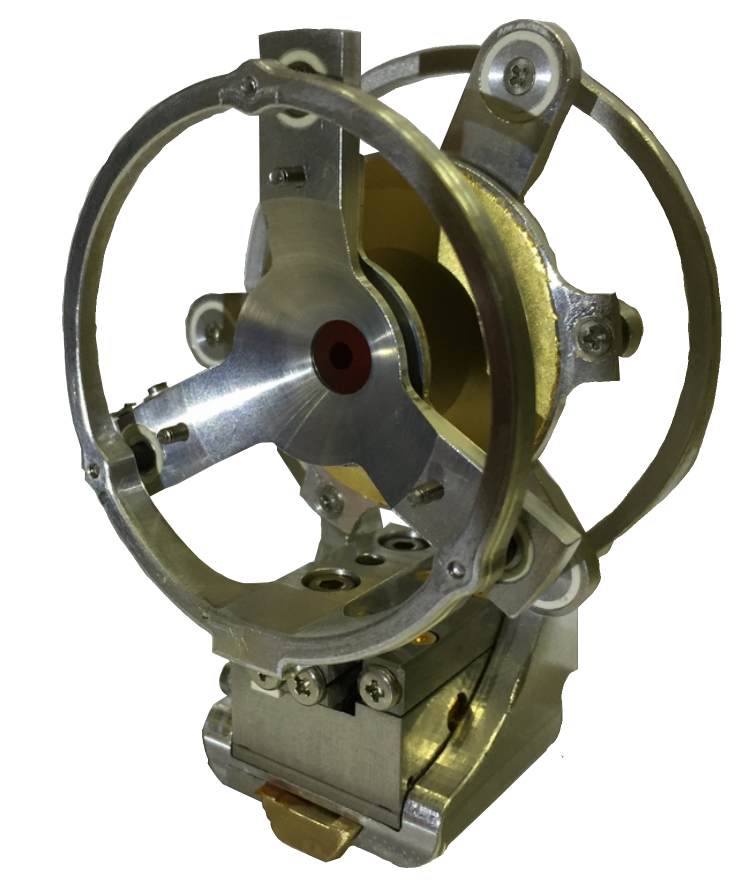
Plunger device
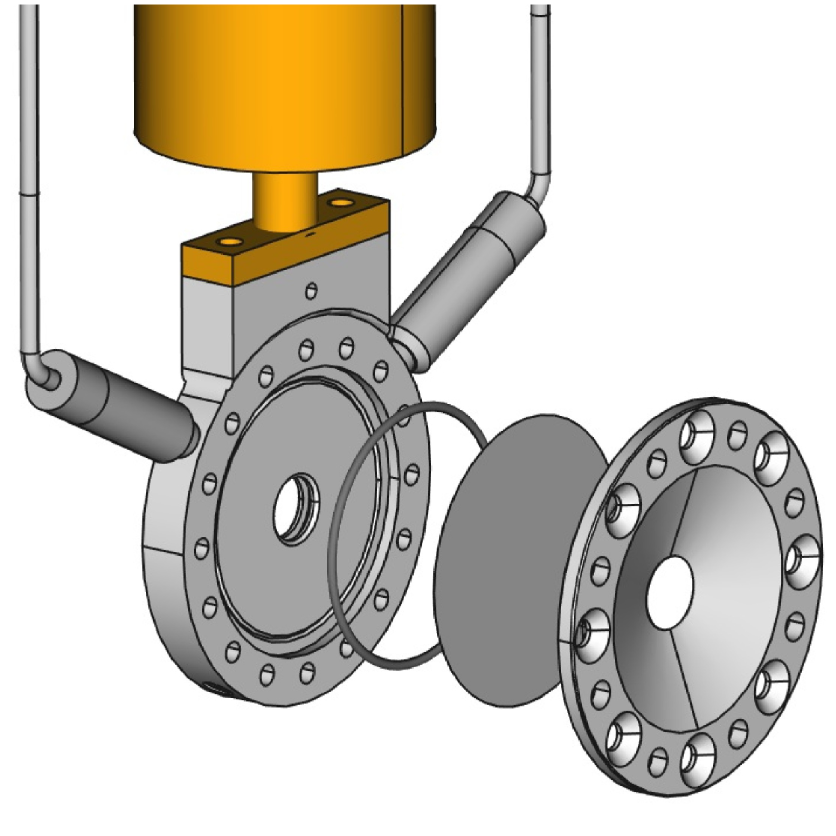
A dedicated Plunger device for lifetime measurements using RDDS technique. Maximum distance of the plunger from the target is 1.2cm. Usage of"reversed plunger" was successfully tested.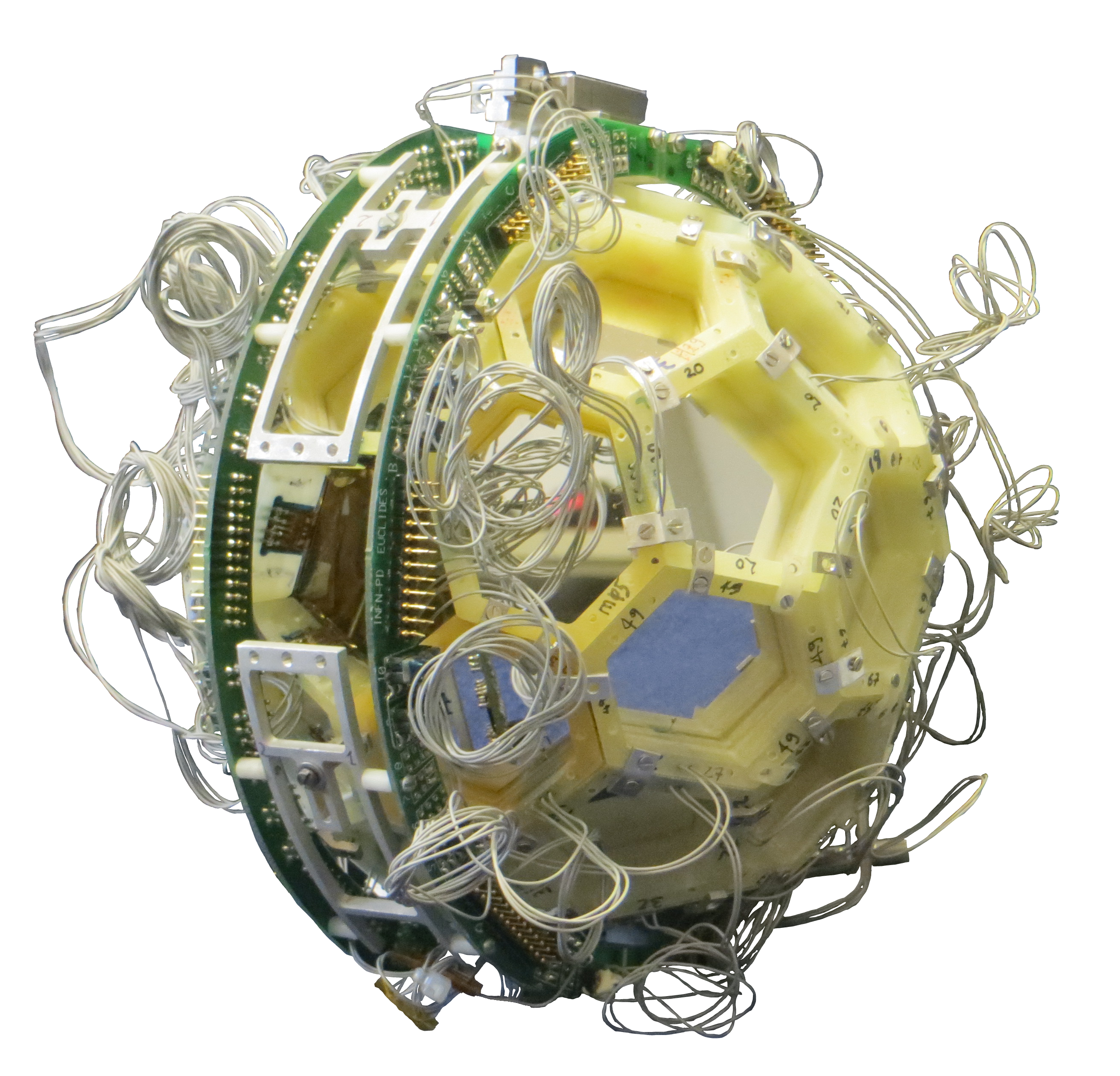
EUCLIDES
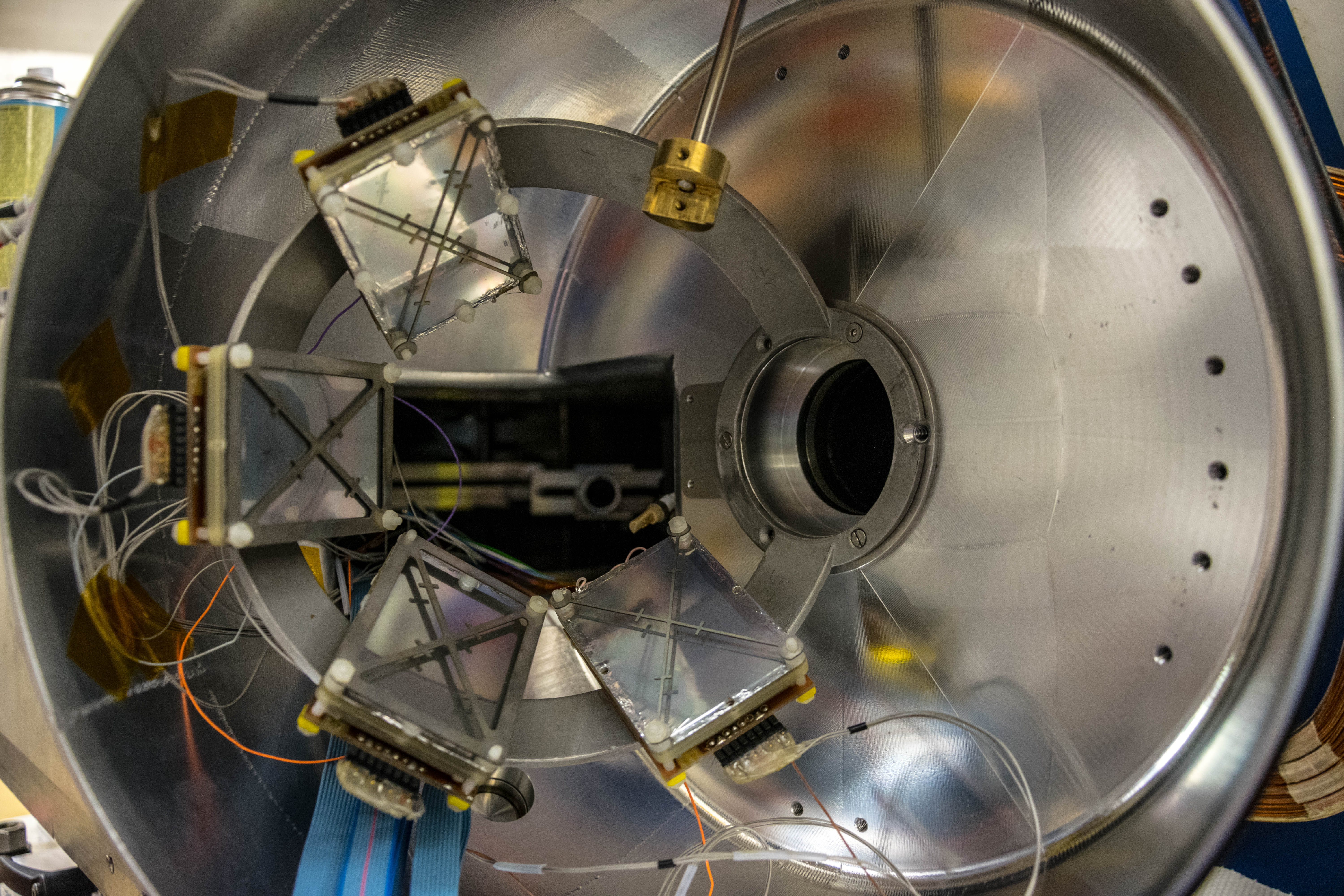
The EUCLIDES array is based on dE-E telescopes, the silicon thickness is 130 μm and 1000 μm for dE and E layers respectively. This allows the discrimination between light charged particles. 40 telescopes form a self-supported structure with the solid angle coverage close to 80% of 4π sr. Detector is made out of pentagonal and hexagonal detectors, the surface of each telescope is approximately 10cm2.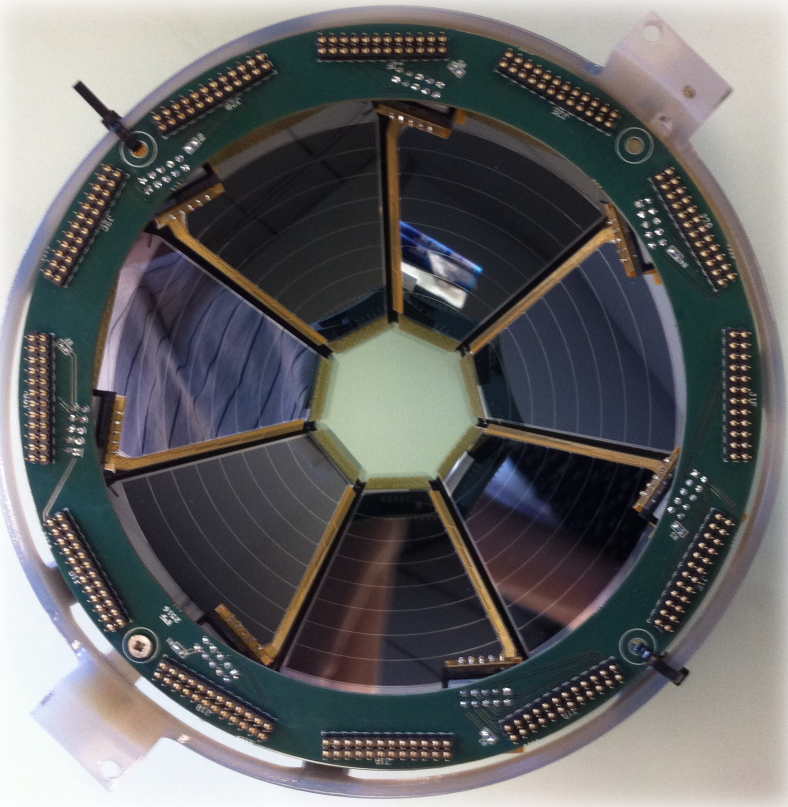
SPIDER
SPIDER is an array of segmented silicon detectors primarily made for heavy-ion detection in low-energy Coulomb-excitation experiments. The array is made out of 7 trapezoidal 300μm thick detectors, each composed of 8 strips. Angular coverage is 124-161° covers 17% of 4π. These values can be however adjusted by changing the distance of the array from the target.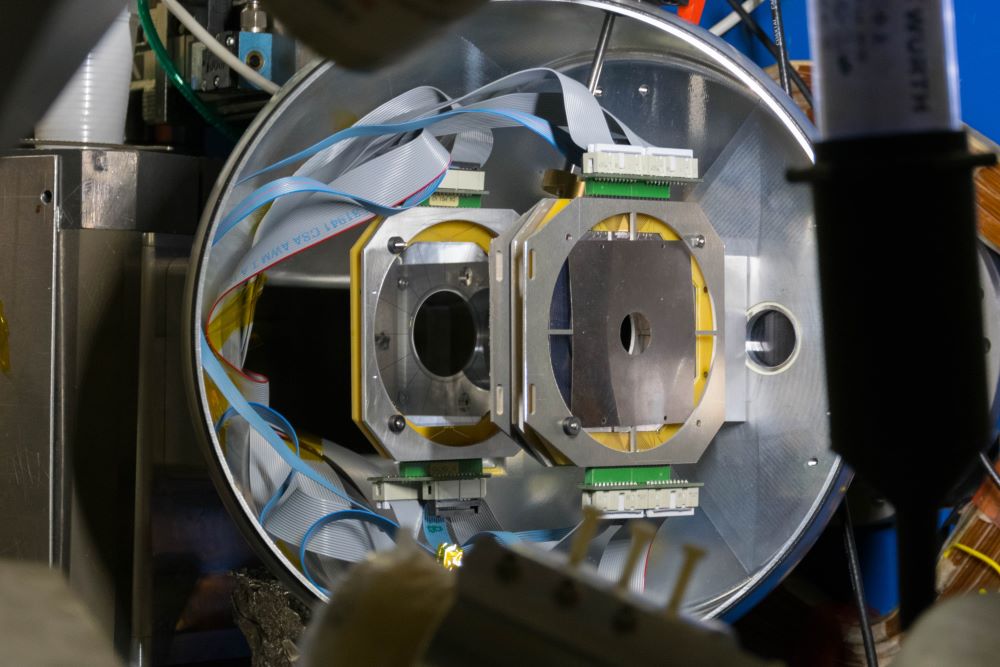
SAURON
SAURON is an annular double-sided silicon stripped ion detector for detection of light charged particles. Junction side is divided into 4 quadrants, each with 16 radial strips; ohmic side is divided into 16 azimuthal strips. Placing detector at standard 5cm distance from the target provides angular coverage of 25-44° if mounted forward, or 136-154° if mounted backward. The distance from the target may be adjusted. Available are 300, 500, 1000 and 1500 μm thick detectors.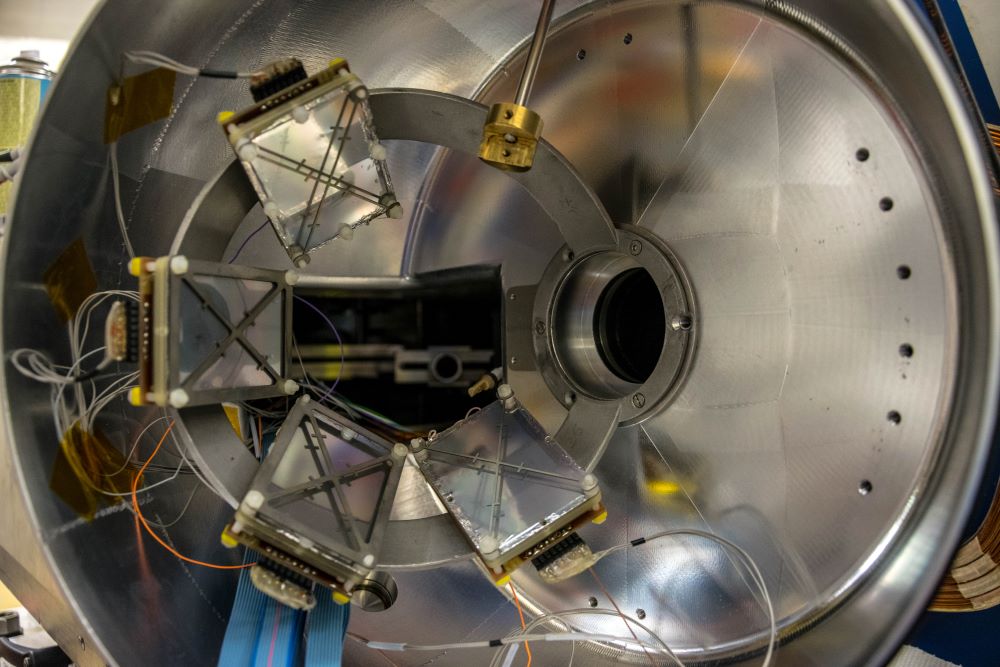
DANTE
DANTE is a position-sensitive array of MCP detectors. Each MCP has, 40 x 60mm2 with position resolution below 1mm and time resolution of 130ps. Individual detectors are mounted on a ring in chevron configuration. Five support rings are available covering various &theta angles, from near-zero to 90°. Additional support for 2 DANTEs, covering θ from ~42 to ~78°, are available for use in conjunction with #SPIDER.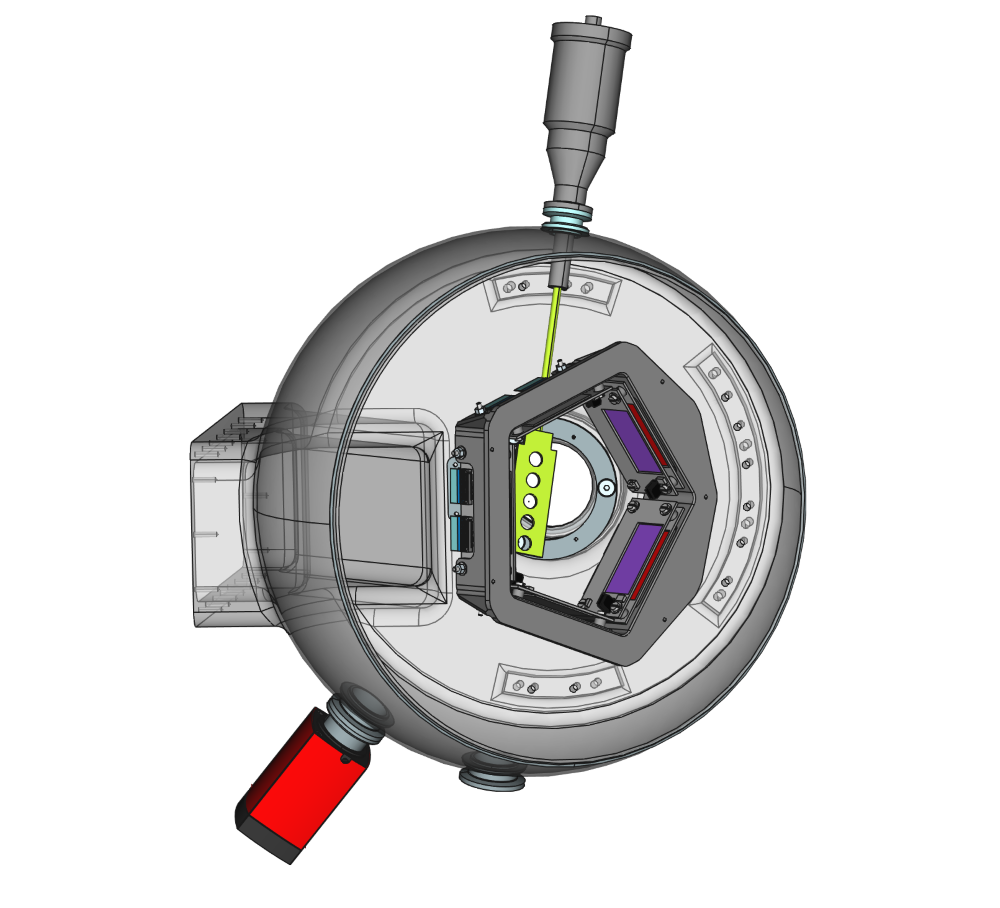
TRACE
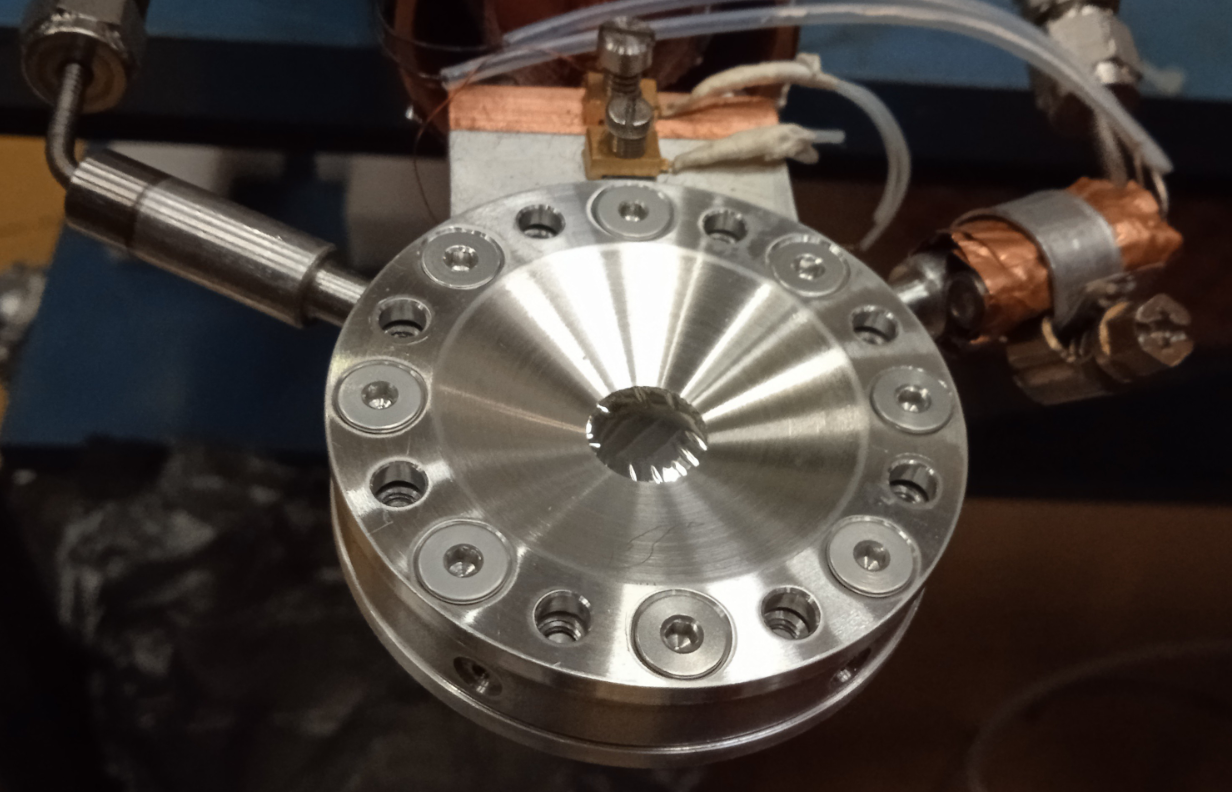
TRACE is an array of highly-segmented silicon telescopes aimed at performing spectroscopy and discrimination of charged particles and light ions in transfer reactions. It is made out of 60 4x4mm square pads arranged in 12x5 configurations. The dE layer is 200μm thick while the E layer is 1-1.5mm thick.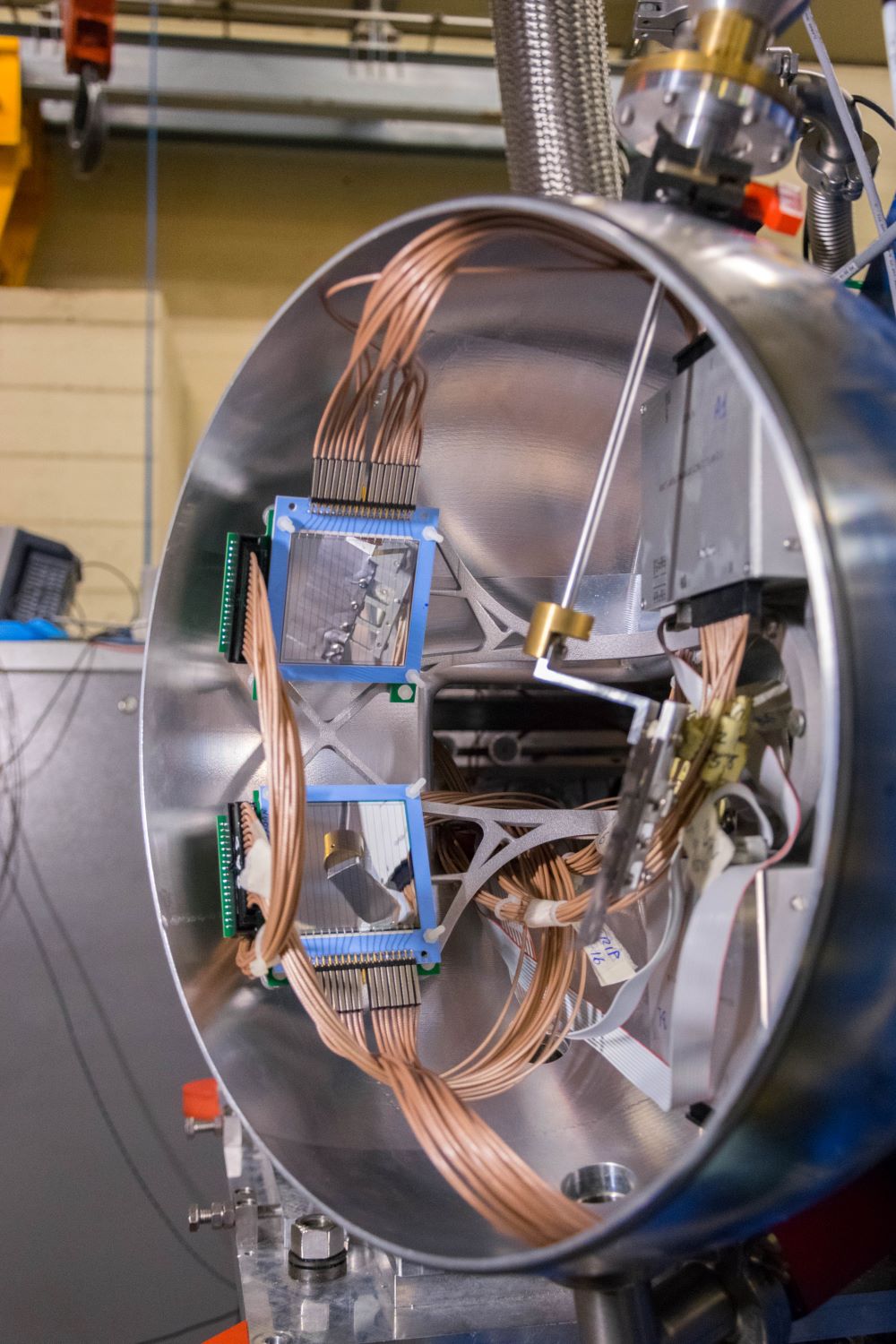

RFD
The Recoil Filter Detector.CTADIR
The goal of the Cryogenic Targets for DIrect Reactions (CTADIR) research project is the construction of cryogenic targets for the study of direct nuclear reactions with the exotic beams produced by the upcoming SPES facility at LNL. The CTADIR project has three research units: INFN-LNL, University of Padova and University of Milan. The INFN-LNL, in particular, is in charge of developing a cryogenic target for 3,4He, designed to be coupled to compact-geometry state-of-the-art detector arrays such as AGATA or GRIT. The cryogenic target has to be kept at temperatures below 10K in order to achieve the desired target density within a limited space of several millimetres.
The project is financed by the PRIN 2017 call for funding.

Publications
Thesis projects
Open projects
The group offers different thesis projects for bachelor, master and PhD thesis.
Below you can find some of the possible topics for your thesis. Contact the corresponding supervisor if you are interested!
Defended theses
Visiting LNL
- If you would like to propose an experiment, check the Useful links section
- If you are planning to come to LNL for experiments or collaboration, you first need to register as LNL user. You can find procedure here
- If you would like to book the LNL- Guesthouse, follow this procedure
- You might also want to check:
- Get to Venice Marco Polo airport
- Reach Padova by train with Trenitalia, or get apps Google Play Apple Store
- Get from Padova to Legnaro with Busitalia, or get apps Google Play Apple Store
People
The group if INFN-LNL works in close collaboration with the group of the University of Padova and INFN-Padova.
Staff:
Postdocs:
PhD students:
Former members:
Useful links
- Get an overview of the LNL accelerators and the different experimental setups
- Take a look at the beam time schedule
- Check the latest developments of the laboratory in the LNL Annual Report
- Become part of the community by registering to the LNL Users Group
- Interested in proposing an experiment with GALILEO or AGATA?
- Check the LNL PAC and the current call for proposals
- Take a look at the possible TANDEM beams and ALPI-PIAVE beams
- Contact a staff member of the group to further discuss your ideas!
- Check out this oldies-but-goldies tools:
- Ion Source and Tandem Setup
- Binary Reaction Kinematics
- Stopping Power for Heavy Ions
- Weisskopf Estimates
- Look at the current job opportunities offered by INFN or check the possible bachelor, master, and PhD thesis offered by the group
- Check the "Galileo Galilei" physics department of the University of Padova
- Take a look at some of the official websites from different INFN sections:
- INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro (LNL)
- INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (LNS)
- INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati (LNF)
- INFN - Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS)
- INFN - Sezione di Firenze (FI)
- INFN - Sezione di Genova (GE)
- INFN - Sezione di Milano (MI)
- INFN - Sezione di Napoli (NA)
- INFN - Sezione di Padova (PD)
- Gamma group Firenze
- Check for the call for proposals of other laboratories:
- Or review the history of gamma-ray spectroscopy by reading about gammapool, or some more information on the HPGe arrays previously hosted by LNL:
- GASP: gasp.lnl.infn.it
- EUROBALL: euroball.lnl.infn.it
- CLARA: clara.lnl.infn.it
- AGATA demonstrator: agata.lnl.infn.it
Useful links
Here you can find a list of tools and resources from INFN-LNL. Most of them require you to login with your INFN CCR-AAI credentials
- To register computers, get access to the LNL gate, etc., contact directly the IT service of LNL by writing to calcolo@lnl.infn.it
- Complete publication list
- Document server Alfresco
- Repository Baltig
- Spotify playlist
- File sender
- Pandora
- Radio-protection source booking
- Cloud Veneto
- The GALILEO wiki
- The GALILEO elog
- The URL shortener
- The L. Vannucci library of LNL
- Call for proposals of other laboratories.